In the hands of a scientist, musical instruments can do many sorts of things. This study tells how some instruments can be used to distinguish between different kinds of physical materials.
“Musical Instruments as Sensors,” Heran C. Bhakta, Vamsi K. Choday, and William H. Grover, ACS Omega, vol. 3, 2018, pp. 11026−11032. The authors, at the University of California, Riverside, report:
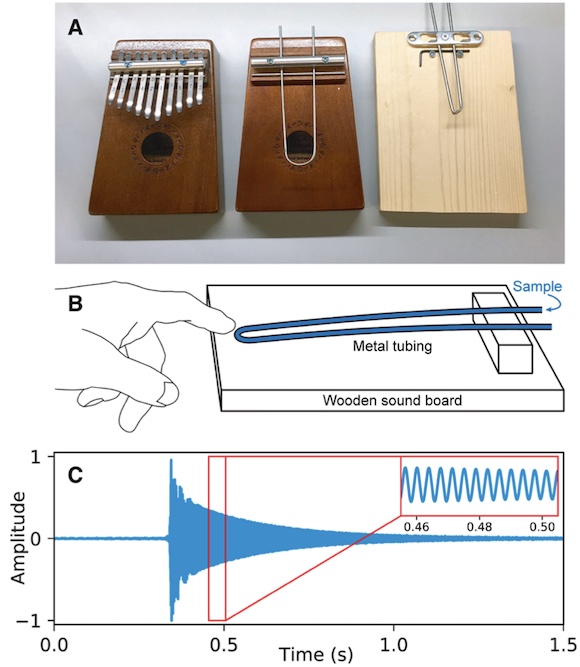
The frequencies of notes made by a musical instrument are determined by the physical properties of the instrument. Consequently, by measuring the frequency of a note, one can infer information about the instrument’s physical properties. In this work, we show that by modifying a musical instrument to contain a sample and analyzing the instrument’s pitch, we can make precision measurements of the physical properties of the sample. We used the mbira, a 3000-year-old African musical instrument that consists of metal tines attached to a wooden board; these tines are plucked to play musical notes. By replacing the mbira’s tines with bent steel tubing, filling the tubing with a sample, using a smartphone to record the sound while plucking the tubing, and measuring the frequency of the sound using a free software tool on our website, we can measure the density of the sample with a resolution of about 0.012 g/mL. Unlike existing tools for measuring density, the mbira sensor can be made and used by virtually anyone in the world. To demonstrate the mbira sensor’s capabilities, we used it to successfully distinguish diethylene glycol and glycerol, two similar chemicals that are sometimes mistaken for each other in pharmaceutical manufacturing (leading to hundreds of deaths).
Here is unrelated video of a more traditional, musical performance on a mbira: